CSAPP_DataLab
Published:
注意可以使用的 op 以及 op 的总个数限制
代码参考:https://github.com/ChenYuHengSJTU/CSAPP_Labs/tree/main/datalab/datalab-handout
1
- 仅使用~和 & 来实现按位异或
- 想法来源:离散数学真值表
/*
* bitXor - x^y using only ~ and &
* Example: bitXor(4, 5) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ &
* Max ops: 14
* Rating: 1
*/
int bitXor(int x, int y) {
int m = (~x) & y;
int n = (~y) & x;
return ~((~m) & (~n));
}
2
- 返回Tmin
/*
* tmin - return minimum two's complement integer
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 4
* Rating: 1
*/
int tmin(void) {
// easy
return (1 << 31);
}
3
- 这题着实把我整崩溃了
- 其实想法并不难,从 Tmax 的特性入手即可
- 0x7fffffff 左移 1 位(即 x*2 = x + x )后加 2 就是 0,当然需要排除 - 1(0xffffffff)的情况,即!!(x+1) 即可
- 但是在处理的过程中,发现给我的答错了
- 百思不得其解
- 后来使用 gdb 考察汇编,发现整个 isTmax 函数只有三行汇编,而且汇编的返回值一定是 0
- 解决方法:把 makefile 中的 - Og 的优化选项去掉,这样编译器才会乖乖算出 (x + x +2) 的值,否则就会优化掉
/*
* isTmax - returns 1 if x is the maximum, two's complement number,
* and 0 otherwise
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | +
* Max ops: 10
* Rating: 1
*/
int isTmax(int x) {
int y = x + x + 2;
return ((!y) & (!!(x + 1)));
}
4
不断配合使用 « 和 ,来构造出 0xaaaaaaaa,x & 0xaaaaaaaa 后,如果确为 allOddbits,应该等于 0xaaaaaaaa,在加上 -0xaaaaaaaa (~0xaaaaaaaa+1),判断是否为 0
/*
* allOddBits - return 1 if all odd-numbered bits in word set to 1
* where bits are numbered from 0 (least significant) to 31 (most significant)
* Examples allOddBits(0xFFFFFFFD) = 0, allOddBits(0xAAAAAAAA) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 2
*/
int allOddBits(int x) {
// even-numbered bits can also be 1
int mask1 = 0xaa;
int mask2 = mask1 << 8;
int mask3 = mask2 << 8;
int mask4 = mask3 << 8;
int mask = (mask1 | mask2 | mask3 | mask4);
// x & mask clears the impact of even-numbered 1s
// to judge whether it equals to 0xaaaaaaaa
return !((x & mask) + (~mask) + 1);
}
5
- 在树状数组中习得
/*
* negate - return -x
* Example: negate(1) = -1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 5
* Rating: 2
*/
int negate(int x) {
// easy
return (~x) + 1;
}
6
- 第一种方法超出的最多运算符数限制
- 第二种方法是取出最低位,然后先判断 0x30 中的 3,再分两种情况讨论最低四位,详见注释
//3
/*
* isAsciiDigit - return 1 if 0x30 <= x <= 0x39 (ASCII codes for characters '0' to '9')
* Example: isAsciiDigit(0x35) = 1.
* isAsciiDigit(0x3a) = 0.
* isAsciiDigit(0x05) = 0.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 3
*/
int isAsciiDigit(int x) {
// my first method run out of all the 15 available ops
// int mask1 = 0xff;
// int mask2 = mask1 << 8;
// int mask3 = mask2 << 8;
// int mask4 = mask3 << 8;
// int mask = (0xc0 | mask2 | mask3 | mask4);
// int c = (x & mask);
// int xx = x & 0x3f;
// int c1 = !(((xx + (~0x30) +1) >> 31) & (0x1)); // == 0
// int c2 = !((((~xx) + 1 + 0x39) >> 31) & (0x1)); // == 0
// return (!c) & (c1 & c2);
// first step is to fetch the low four bits
int mask = 0xf;
int low = mask & x;
// then judge the upper 28 bits;use ^ to judge whether it equals to 0x30
int xx = x + (~low) +1;
int c = xx ^ 0x30;
// two cases of the low four bits
// 0xxx or 1000 or 1001
int mid = low & 0x6;
int high = low >> 3;
return (!c) & ((!high) | (!mid));
}
7
- 需要一个小 trick:!!x 将 x 转换为 0 或 1
- 还有就是,得到 0 或 1 后,怎么转换为 0xffffffff,因为我们要用 0xffffffff & y 或 0xffffffff & z 来得到 y 和 z。
- 还是利用 0,1,-1 之间的位级关系
/*
* conditional - same as x ? y : z
* Example: conditional(2,4,5) = 4
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 16
* Rating: 3
*/
int conditional(int x, int y, int z) {
// use ! to judge , to change odinary nums to 0 or 1
// after we get 0 or 1
// for 0 : we can use !x to change it to 1 , then ~x + 1 to get -1 , with
// all bits of 1
// for 1 : we can use !!x to change it back to 1, then ~x+1 to get -1
return ((~(!(!x)) + 1) & y) | ((~(!x) + 1) & z);
}
8
- 判等:^
- 基本想法就是作差判断符号
- 但是需要考虑溢出,仅需考虑正数减负数的溢出
- 使用符号位判断溢出的特殊情况
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
// use ^ to judge equalance
// to avoid overflow , use the most significant bit to deal with different cases
int xs = x >> 31;
int ys = y >> 31;
return (!(x ^ y)) | (xs & (!ys)) | ((!(xs ^ ys)) & (x + (~y) +1) >> 31);
}
9
- 实现逻辑非
- 把数值分为三类:positive,negative,zero
- 取 x 与 - x 的符号位,在进行 & 0x1(因为对负数实行逻辑右移)+ 1,得到 xs 与 negxs
- 对于非零值,两者一定有一者为 0
- 对于零,两者均为 1
/*
* logicalNeg - implement the ! operator, using all of
* the legal operators except !
* Examples: logicalNeg(3) = 0, logicalNeg(0) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
int logicalNeg(int x) {
// we divide all x into three groups: 0,positive,negative
// for negative and positive,one and only one of the significant bit of x and -x will be 1
// but for 0,they are all 0
// so we add 1 ,keep the trait for positive and negative numbers,but change the case of 0
// last,for non-zero : xs == 0 && negxs == 1 || xs == 1 && negxs == 0
// for zero : xs == 1 || negxs == 1
int xs = (((x >> 31) & 0x1) + 1) & 0x1 ;
int negxs = (((((~x) + 1) >> 31) & 0x1) + 1) & 0x1 ;
return xs & negxs;
}
10
- kind of hard
/* howManyBits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in
* two's complement
* Examples: howManyBits(12) = 5
* howManyBits(298) = 10
* howManyBits(-5) = 4
* howManyBits(0) = 1
* howManyBits(-1) = 1
* howManyBits(0x80000000) = 32
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 90
* Rating: 4
*/
int howManyBits(int x) {
int isZero = !x;
int mask = ((!!x) << 31) >> 31;
int flag = x >> 31;
x = ((~flag) & x) | (flag & (~x));
int bit_16, bit_8, bit_4, bit_2, bit_1, bit_0;
bit_16 = (!((!!(x >> 16)) ^ 0x1)) << 4;
x >>= bit_16;
bit_8 = (!((!!(x >> 8)) ^ 0x1)) << 3;
x >>= bit_8;
bit_4 = (!((!!(x >> 4)) ^ 0x1)) << 2;
x >>= bit_4;
bit_2 = (!((!!(x >> 2)) ^ 0x1)) << 1;
x >>= bit_2;
bit_1 = (!((!!(x >> 1)) ^ 0x1));
x >>= bit_1;
bit_0 = x;
int res = bit_16 + bit_8 + bit_4 + bit_2 + bit_1 + bit_0 + 1;
return (isZero | (mask & res));
}
11
- 浮点数的三道题均不难,更多的是考察对于 IEEE754 浮点数标准的理解记忆
- 第一题,分情况(规格化,非规格化,NAN)讨论即可
/*
* floatScale2 - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatScale2(unsigned uf) {
int expmask = 0xff << 23;
int s = uf >> 31;
int fmask1 = 0xff;
int fmask2 = fmask1 << 8;
int fmask3 = fmask2 << 7;
int fmask = fmask1 | fmask2 | fmask3;
int frac = uf & fmask;
int exp = (uf & expmask) >> 23;
if(exp && (exp - 0xff))
exp = exp + 1;
if(!exp)
frac = frac << 1;
uf = (s << 31) | (exp << 23) | (frac);
return uf;
}
12
- 也是只需分情况讨论即可,注意 exp 位域的最大值为 1111110,不能是 1111111
- 从这道题中可以 get 到,对于溢出,均处理为 inf,而不是 NAN
/*
* floatFloat2Int - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (int) f
* for floating point argument f.
* Argument is passed as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point value.
* Anything out of range (including NaN and infinity) should return
* 0x80000000u.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
int floatFloat2Int(unsigned uf) {
int expmask = 0xff << 23;
int exp = (uf & expmask) >> 23;
int s = uf >> 31;
int fmask1 = 0xff;
int fmask2 = fmask1 << 8;
int fmask3 = fmask2 << 7;
int fmask = fmask1 | fmask2 | fmask3;
int frac = uf & fmask;
int M;
int E;
int bias = 127;
if(exp == 0xff){
return 0x80000000u;
}
if(exp && (exp - 0xff)){
M = 1 << 23 | frac;
E = exp - bias;
}
else{
M = frac;
E = 1 - bias;
}
int res;
if(E > 23){
res = M << E;
// do not forget this anything out of range
if(E >= 8) return 0x80000000u;
}
else if(E == 23) res = M;
else{
int e = 23 - E;
if(e >= 24) return 0;
res = M >> (23 - E);
}
if(s) return -res;
return res;
}
13
- 特别注意 float 的表示范围,是不对称的,既要考虑规格化,也要考虑非规格化
- 具体细节可以看书
/*
* floatPower2 - Return bit-level equivalent of the expression 2.0^x
* (2.0 raised to the power x) for any 32-bit integer x.
*
* The unsigned value that is returned should have the identical bit
* representation as the single-precision floating-point number 2.0^x.
* If the result is too small to be represented as a denorm, return
* 0. If too large, return +INF.
*
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. Also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
#include<stdio.h>
unsigned floatPower2(int x) {
int exp;
int frac;
int s = 0;
int res = 0;
if(x >= 128){
exp = 0xff;
frac = 0;
s = 0;
}
else if(x < -126 - 23){
frac = 0;
exp = 0;
}
else if(x >= -126 - 23 && x <= -127){
exp = 0;
frac = 1 << (x - (-126 - 23));
}
else {
frac = 0;
exp = 127 + x;
}
res = (exp << 23) | (frac) | (s << 31);
return res;
}
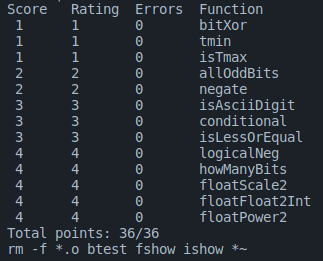
Evaluation
./run.sh